Understanding Hiatal Hernia and GERD
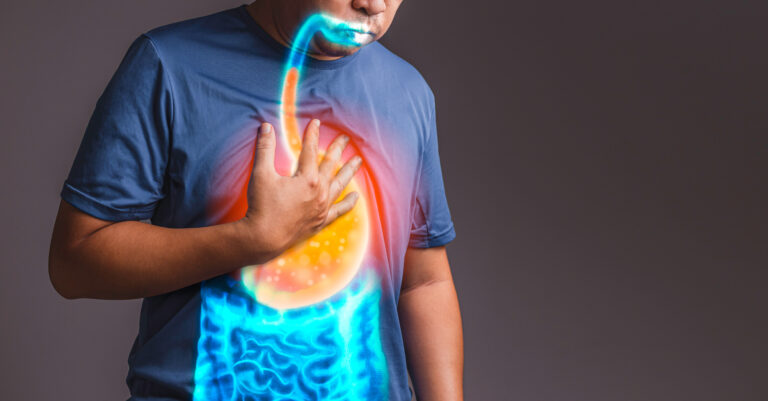
A hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are both significant medical conditions that affect the upper gastrointestinal tract. A hiatal hernia occurs when a portion of the stomach becomes displaced into the chest cavity. This displacement can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the muscle responsible for preventing stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. When the LES becomes compromised, it can lead to GERD.
GERD is a chronic condition characterized by the frequent and often painful reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus. This backflow can result in symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. Over time, GERD can lead to esophageal damage and increase the risk of more serious complications, including esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, and even esophageal cancer.
These conditions can occur separately, but they are often interconnected and occur together. Understanding the connection between hiatal hernia and GERD is crucial for effective diagnosis and management. Hiatal hernias can contribute to the development or exacerbation of GERD by disrupting the normal anatomy of the lower esophagus and weakening the LES.
Treatment options range from lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medications to surgical procedures. Effective management of these conditions requires a tailored approach and close collaboration with healthcare professionals to alleviate symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
Malladi Bariatrics has expertise in managing both GERD and hiatal hernias, so you can get relief from them and the treatment you need to move forward with better health and less discomfort. A misdiagnosed hiatal hernia can be a frustrating experience and can even have you fearing a heart attack or other serious health condition. Working with us can solve the problem, reducing your anxiety and giving you less pain and more peace of mind.
Hiatal Hernia: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
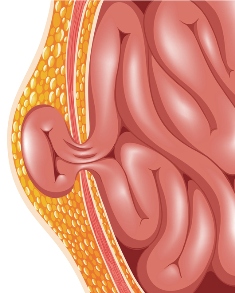
A hiatal hernia is a medical condition that occurs when a portion of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm and into the chest cavity. The diaphragm is a large muscle that separates the chest and abdominal cavities, and it has an opening called a hiatus, through which the esophagus passes to connect to the stomach. When this opening weakens or enlarges, it can lead to a hiatal hernia. There are two main types of hiatal hernias. These are sliding hiatal hernias and paraesophageal hiatal hernias.
The exact cause of hiatal hernias is not always clear, but several factors can contribute to their development. These factors include:
- Age: Hiatal hernias are more common in people over the age of 50.
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase pressure on the abdomen and weaken the diaphragm.
- Inherited traits: Genetics may play a role in a person’s susceptibility to hiatal hernias.
- Frequent heavy lifting: Activities that involve lifting heavy objects can strain the abdominal muscles and increase the risk of herniation.
Symptoms of hiatal hernias can vary in severity and may include:
- Heartburn: The most common symptom is a burning sensation in the chest, often after eating or when lying down.
- Acid reflux: Stomach acid can flow back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and potential damage to the esophageal lining.
- Difficulty swallowing: In some cases, the herniated portion of the stomach can compress the esophagus, making it harder to swallow.
- Chest pain: Hiatal hernias may cause chest pain, which can sometimes be mistaken for heart-related issues.
- Belching and hiccups: Increased belching or frequent hiccups can be a sign of a hiatal hernia.
Diagnosing hiatal hernias typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Medical professionals might perform a barium swallow or an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy to visualize the hernia and assess its size and position. These tests can also identify any inflammation or damage to the esophagus caused by acid reflux.
Treatment options for hiatal hernias depend on the severity of symptoms and the size of the hernia. Lifestyle changes such as losing weight, avoiding large meals before bedtime, and elevating the head of the bed, can help alleviate symptoms. Over-the-counter or prescription medications may also be recommended to manage heartburn.
In many cases, hiatal hernia surgery is necessary to repair the hernia and prevent complications. Dr. Preeti Malladi can perform the appropriate diagnostic tests to determine if you have a hiatal hernia, then ensure you get the right treatment to address the problem and alleviate your discomfort.
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease): Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), often referred to as acid reflux, is a chronic medical condition that affects the digestive system. It occurs when stomach acid frequently flows backwards into the esophagus, causing irritation and various uncomfortable symptoms. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of GERD is essential for managing this common disorder.
GERD primarily stems from a malfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscular ring that separates the esophagus from the stomach. Normally, the LES closes tightly after food passes through it, preventing stomach acid from moving upward. However, in people with GERD, the LES weakens or relaxes inappropriately, allowing acid to escape. Several factors contribute to this weakening, including:
- Diet: Consuming acidic, spicy, or fatty foods can relax the LES and trigger symptoms.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts pressure on the stomach, pushing acid into the esophagus.
- Hiatal Hernia: This condition, where the upper part of the stomach protrudes into the chest cavity, can weaken the LES.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased abdominal pressure during pregnancy can lead to GERD.
- Smoking and Alcohol: These substances can relax the LES and aggravate symptoms.
GERD symptoms can vary in severity and may include:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating or at night.
- Regurgitation: Sour-tasting fluid or food may come back up into the mouth.
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing, often due to esophageal irritation.
- Chronic Cough: GERD can cause a persistent, dry cough.
- Sore Throat: The acid can irritate the throat, leading to a scratchy or sore feeling.
- Hoarseness: Chronic irritation can affect the vocal cords.
- Chest Pain: Sometimes, GERD symptoms can mimic heart-related chest pain, causing confusion and anxiety.
Diagnosing GERD typically involves a combination of medical history, symptom assessment, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers may perform the following:
- Medical History: Patients discuss their symptoms, diet, lifestyle, and medical history, which can often provide valuable insights.
- Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth into the esophagus to directly visualize any damage caused by GERD.
- pH Monitoring: This test measures the acid levels in the esophagus over a 24-hour period, providing information on the frequency and severity of acid reflux.
- Esophageal Manometry: This test assesses the function of the esophagus and LES by measuring pressure and muscle contractions.
- Barium Swallow X-ray: Patients swallow a barium solution, and X-rays are taken to identify any structural abnormalities or signs of reflux.
- GERD Questionnaires: Standardized questionnaires can help assess symptom severity and response to treatment.
GERD is a chronic condition that often requires long-term management through lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medications. Some cases will need surgical intervention. Early diagnosis and effective management are key to alleviating symptoms and preventing complications, such as esophageal damage or Barrett’s esophagus, which can increase the risk of esophageal cancer. If you have symptoms of GERD, it’s very important to understand what foods you should and shouldn’t eat, along with making any other recommended changes.
Differentiating Hiatal Hernia and GERD
While hiatal hernias and GERD share some symptoms like heartburn, they are fundamentally different in terms of their causes, mechanisms, and treatments. Hiatal hernia is a structural issue where the opening in the diaphragm becomes too large and allows part of the stomach to protrude into the chest cavity. GERD, on the other hand, is a chronic digestive disorder characterized by the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus. It is not a structural issue but rather a functional problem involving the lower esophageal sphincter.
A thorough medical evaluation is vital for an accurate diagnosis. And the right diagnosis is needed for effective treatment that relieves symptoms and reduces the risk of serious damage.
Treatment Options with Malladi Bariatrics & Advanced Surgery
Treatment options for GERD and hiatal hernia vary based on the severity of symptoms and other factors, with treatment options being lifestyle modifications, medications, and surgery.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Patients are often advised to make dietary and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms. This includes avoiding large meals, acidic and spicy foods, and tight clothing. Elevating the head of the bed and losing weight can also help reduce symptoms.
- Medications: Antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and H2 blockers are sometimes prescribed to reduce stomach acid production and alleviate heartburn and reflux.
- Surgery: Lifestyle changes and medications don’t address the root cause of GERD which is the weakness of the LES. Surgical intervention is often the most effective option for long term relief of symptoms. Laparoscopic techniques are often used for a quicker recovery.
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the problem, patient preferences, and a doctor’s recommendation. A combination of approaches may be most effective to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Malladi Bariatrics offers both surgical and non-surgical solutions to provide relief for patients with either one or both of these uncomfortable conditions.
Choosing Malladi Bariatrics for Hiatal Hernia and GERD Care
When you’re experiencing a digestive disorder, Malladi Bariatrics is here to help. We are your trusted healthcare provider for GERD, hiatal hernias, and other digestive or gastrointestinal issues. Dr. Preeti Malladi and her team understand your concerns and discomfort and will be here to answer your questions and help you choose the right treatment option for your needs.
With a patient-centered approach and personalized treatment plans, we can have you feeling more like yourself again. Get in touch with us today by using our online contact form to seek expert consultation for your hiatal hernia or GERD concerns.