What is Minimally Invasive Surgery?
According to the American Institute for Minimally Invasive Surgery, MIS is essentially the use of smaller incisions, that results in fewer stitches, which leads to a faster patient recovery. That’s it! But in some situations, a minimally invasive surgery would not be as effective as a traditional surgery, so it is best to consult with a surgeon who is properly trained in minimally invasive procedures so they can help determine the best long-term medical solution for your particular situation. So while the thought of minimally invasive techniques sounds good, the benefits of smaller incisions and fewer stitches may not outweigh the lower effectiveness of that procedure in certain instances, in which a more traditional approach may be best in the long run. Rest assured that our Dallas and Plano-based practice applies a holistic, consultative and collaborative approach to our patient’s situations, and crafts an individual surgical solution that is customized just for you.
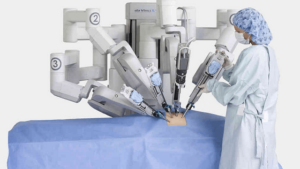
Robotic Surgery
Robotic systems are becoming increasingly popular in the medical fraternity owing to the unique advantages including the precision, safety and many other advantages.
The da Vinci® robotic surgical system is one of the popular and widely employed robotic systems in the specialty of medicine and is used to perform surgical procedures in general surgeries and other specialties of medicine. The da Vinci ® system offers a minimally invasive alternative option to traditional open and laparoscopic surgery. Most of the complex surgical procedures may be performed with the da Vinci ® robotic system. Traditional open surgery uses a large incision and patients may experience complications such as pain, damage to the surrounding organs and nerves and long recovery period. In contrast, the daVinci ®robotic system is the most effective and least invasive technique which ensures faster recovery with minimal pain and minimal risks as compared with traditional open surgery.
The da Vinci ® surgical system consists of a surgeon’s console, a patient-side cart with four interactive robotic arms, a high-performance vision system (3D camera) and miniaturized EndoWrist surgical instruments.
While performing the surgical procedure your surgeon will be seated at the da Vinci ® console and is able to view a magnified, high-resolution 3D image of the area to be operated. To access the surgical site your surgeon introduces miniaturized EndoWrist instruments through few tiny incisions. These instruments help your surgeon perform the procedure with precision and control. Your surgeon uses master controls that function similar to forceps and in turn da Vinci ® responds by immediate translation of surgeon’s directions into precise movements of miniaturized instruments.
The da Vinci ® robotic system offers several advantages over the traditional surgery including less pain, low risk of infection, fewer complications, less scarring, less blood loss, short hospital stay and faster recovery.
The da Vinci ® Robot System is considered safe and effective, but may not be appropriate for everyone. It is contraindicated in patients with bleeding disorders, history of previous surgery, pregnancy and cardiopulmonary diseases. Always discuss with your doctor about all treatment options suitable for you, as well as the benefits and risks.
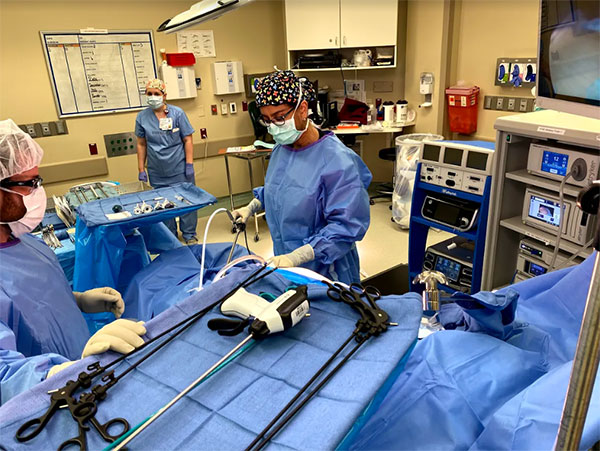
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopy can used for both diagnostic and operative purposes.
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
A laparoscopy is diagnostic when the surgeon is viewing the abdominal cavity to make a diagnosis, without any treatment administered at that time. This is particularly useful when other tests such as x-rays, scans, or blood work are inconclusive. The laparoscope is usually smaller as no channel is needed for surgical instruments.
Operative Laparoscopy
A laparoscopy is considered operative when the surgeon is treating a problem that is found during diagnostic laparoscopy with surgical instruments through the laparoscope.
If your surgeon sees an opportunity to repair a problem during a diagnostic Laparoscopy, an operative Laparoscopy will usually be performed at that time depending on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s preference.
Types of Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures
Types of minimally invasive operative procedures that can be performed with Laparoscopy include the following:
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Removal of the gallbladder
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Removal of the appendix
- Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: Repair of common hernia sites including inguinal (groin), femoral (below the groin), and some abdominal hernias.
- Laparoscopic Splenectomy: Removal of the spleen
- Laparoscopic Adhesiolysis: Removal and freeing of scar tissue build up, also called adhesions.
- Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery: Certain weight loss surgeries can be performed laparoscopically including adjustable gastric banding and gastric bypass surgeries.
- Laparoscopic Colectomy: Surgical removal of part of the colon for treatment of a wide range of colorectal diseases such as colon cancer, diverticulitis, chronic ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease.
- Laparoscopic GERD surgery: Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be treated laparoscopically.
- Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy: Removal of the adrenal glands
- Laparoscopic Nephrectomy: Removal of a kidney for donor purposes.
Laparoscopy is performed as day surgery either in the hospital or outpatient surgery center under general, regional, or occasionally local anesthesia depending on the type of procedure performed and the surgeon’s preference. During laparoscopy, the patient is placed lying on their back with their body tilted so the feet are higher than the head. This position helps to move some of the abdominal organs toward the chest allowing the surgeon a clearer view.
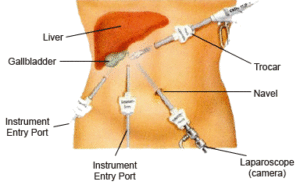
The surgeon uses a needle to inject a harmless gas into the abdominal cavity near the belly button to expand the viewing area of the abdomen giving the surgeon a clear view and room to work.
The surgeon makes a small incision in the abdomen, usually at or below the belly button, and inserts a tube called a trocar through which the laparoscope is introduced into the abdomen.
Additional small incisions may be made for a variety of surgical instruments to be used during the procedure. The location of the incisions will depend upon the reason for the procedure.
With the images from the laparoscope as a guide, the surgeon can look for any pathology or anomaly.
The large image on the television screen allows the surgeon to see the abdominal contents directly and to determine the extent of the problem, and then perform the particular surgical procedure, if necessary.
If the surgeon sees an opportunity to treat a problem, a variety of surgical instruments can be inserted through the laparoscope or through other small incisions your surgeon may make.
After treating the problem, the laparoscope and other instruments are removed and the gas released.
The tiny incisions are closed and covered with small bandages.
Laparoscopy is much less traumatic to the muscles and soft tissues than the traditional method of surgically opening the abdomen with long incisions (open techniques).
Specific complications for Laparoscopy include:
- Post-operative fever and infection
- Surgical injury to blood vessels
- Surgical injury to bowel or bladder
- Gas Embolism
- Blood Clots
- Adhesions
- Conversion to Laparotomy: There are occasions when a laparoscopy cannot be completed successfully without converting to a traditional “open” surgery called a laparotomy. A laparotomy is similar but is done through a larger abdominal incision.
Contact our Plano or Dallas Bariatrics and Advanced Surgery Clinic to schedule an appointment in the DFW area or to learn more information about how we can help you.